Structural - Command Pattern
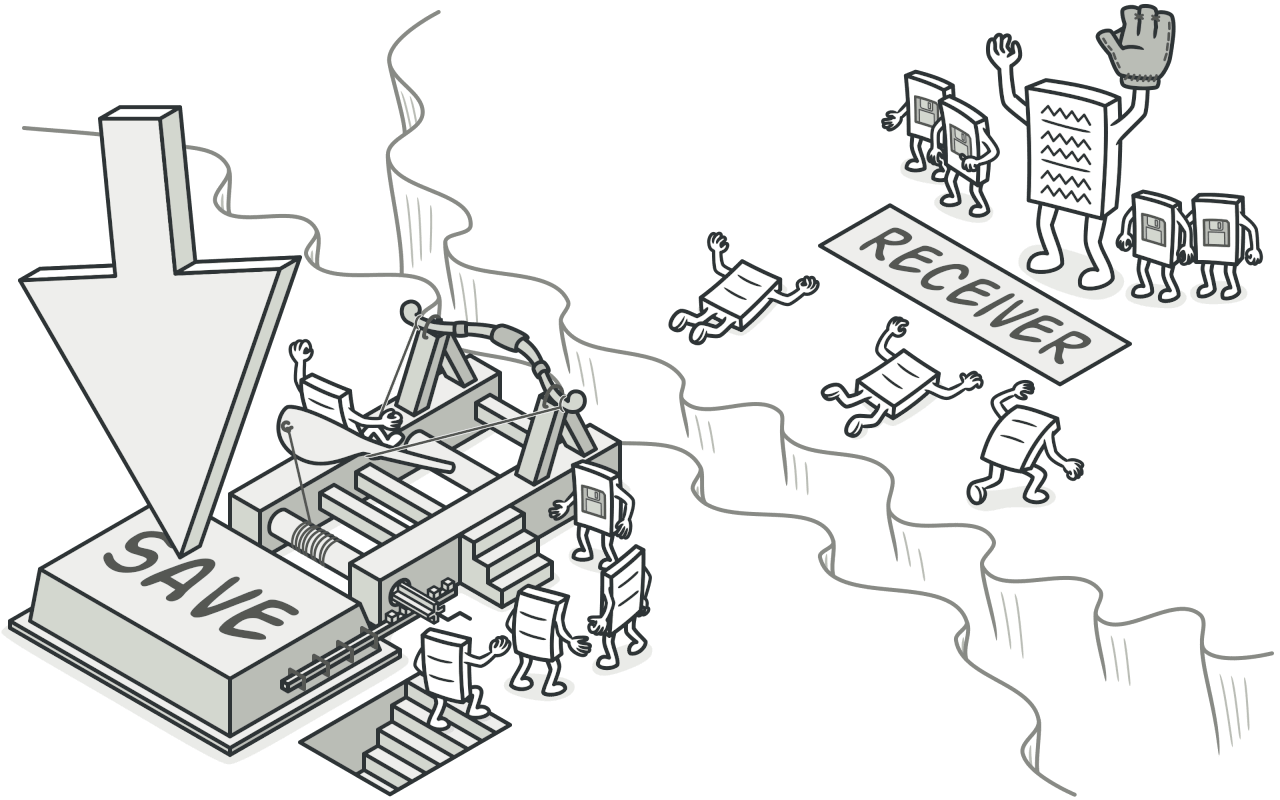
Design Thoughts
The Command pattern is a behavioral design pattern that transforms a request into a separate object that contains all the information related to the request. This transformation allows you to parameterize methods based on different requests, delay or queue requests, and implement revocable operations.
The Command pattern usually involves the following roles:
-
Command interface: defines the interface for performing operations.
-
Concrete Command class: implements the command interface and encapsulates the specific logic for performing operations.
-
Invoker: responsible for calling the command object to execute the request.
-
Receiver: knows how to implement the operations related to executing a request.
-
Client: creates a concrete command object and sets its receiver.
Class Diagram
Code Implementation
interface Command {
void execute();
}
class Invoker {
private Command command;
public void setCommand(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void executeCommand() {
this.command.execute();
}
}
class Receiver {
public void operation(Object... params) {
System.out.println("Receiver operation invoke.");
}
}
class ConcreteCommand implements Command {
private Receiver receiver;
private Object[] params;
public ConcreteCommand(Receiver receiver, Object[] params) {
this.receiver = receiver;
this.params = params;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("ConcreteCommand execute invoke.");
this.receiver.operation(this.params);
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Receiver receiver = new Receiver();
Command command = new ConcreteCommand(receiver, new Object[] {});
Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
invoker.setCommand(command);
invoker.executeCommand();
}
}Pros and Cons
Advantages:
- In line with the single responsibility principle, the command pattern decouples the caller and the receiver, making the objects in the system more independent. The caller does not need to know the specific implementation of the receiver, but only needs to know how to use the command object.
- In line with the open-closed principle, new command classes can be easily added to the system without modifying the existing code. This makes the system easier to expand and maintain.
Disadvantages:
- Each specific command requires a corresponding command class, which may increase the number of classes and make the system complicated.
Applicable Scenarios
- In graphical user interfaces, menu and button click operations usually use the command pattern to encapsulate different operations into command objects.
- When you need to support multi-level undo and redo operations, the command pattern is a common choice.
- Remote controls usually use the command pattern, with each button corresponding to a command to control the device.
- The command pattern can be used to implement task scheduling and queue systems, putting command objects into queues and executing them in sequence.
- In database systems, the command pattern can be used to manage transaction execution and rollback to ensure the consistency of a series of database operations.
The command pattern is suitable for scenarios that require decoupling callers and receivers, supporting undo and redo, supporting command queuing, queues, and logs. In appropriate scenarios, the command pattern can improve the flexibility and maintainability of the system.